Naevi Average ratng: 6,2/10 5916 votes
Old Navy provides the latest fashions at great prices for the whole family. Shop men's, women's, women's plus, kids', baby and maternity wear. We also offer big and tall sizes for adults and extended sizes for kids. Pigmented nevi (moles) are growths on the skin that usually are flesh-colored, brown or black. Moles can appear anywhere on the skin, alone or in groups.
Giant congenital melanocytic nevus is a skin condition characterized by an abnormally dark, noncancerous skin patch (nevus) that is composed of pigment-producing cells called melanocytes. It is present from birth (congenital) or is noticeable soon after birth. The nevus may be small in infants, but it will usually grow at the same rate the body grows and will eventually be at least 40 cm (15.75 inches) across. The nevus can appear anywhere on the body, but it is more often found on the trunk or limbs. The color ranges from tan to black and can become darker or lighter over time. The surface of a nevus can be flat, rough, raised, thickened, or bumpy; the surface can vary in different regions of the nevus, and it can change over time.
The skin of the nevus is often dry and prone to irritation and itching (dermatitis). Excessive hair growth (hypertrichosis) can occur within the nevus. There is often less fat tissue under the skin of the nevus; the skin may appear thinner there than over other areas of the body.People with giant congenital melanocytic nevus may have more than one nevus (plural: nevi). The other nevi are often smaller than the giant nevus. Affected individuals may have one or two additional nevi or multiple small nevi that are scattered over the skin; these are known as satellite or disseminated nevi.Affected individuals may feel anxiety or emotional stress due to the impact the nevus may have on their appearance and their health.
Children with giant congenital melanocytic nevus can develop emotional or behavior problems.Some people with giant congenital melanocytic nevus develop a condition called neurocutaneous melanosis, which is the presence of pigment-producing skin cells (melanocytes) in the tissue that covers the brain and spinal cord. These melanocytes may be spread out or grouped together in clusters. Their growth can cause increased pressure in the brain, leading to headache, vomiting, irritability, seizures, and movement problems. Tumors in the brain may also develop.Individuals with giant congenital melanocytic nevus have an increased risk of developing an aggressive form of called, which arises from melanocytes. Estimates vary, but it is generally thought that people with giant congenital melanocytic nevus have a 5 to 10 percent lifetime risk of developing melanoma.
Melanoma commonly begins in the nevus, but it can develop when melanocytes that, such as those in, become cancerous. When melanoma occurs in people with giant congenital melanocytic nevus, the survival rate is low.Other types of tumors can also develop in individuals with giant congenital melanocytic nevus, including soft tissue tumors , fatty tumors (lipomas), and tumors of the nerve cells (schwannomas). Gene mutations cause most cases of giant congenital melanocytic nevus. Skidstorm android. Rarely, mutations in the gene are responsible for this condition.The proteins produced from these genes are involved in a process known as signal transduction by which signals are relayed from outside the cell to the cell's. Signals relayed by the N-Ras and BRAF proteins instruct the cell to grow and divide (proliferate) or to mature and take on specialized functions (differentiate). To transmit signals, these proteins must be turned on; when the proteins are turned off, they do not relay signals to the cell's nucleus.The NRAS or BRAF gene mutations responsible for giant congenital melanocytic nevus are somatic, meaning that they are acquired during a person's lifetime and are present only in certain cells. These mutations occur early in embryonic development during the growth and division (proliferation) of cells that develop into.
Somatic NRAS or BRAF gene mutations cause the altered protein in affected cells to be constantly turned on (constitutively active) and relaying signals. The overactive protein may contribute to the development of giant congenital melanocytic nevus by allowing cells that develop into melanocytes to grow and divide uncontrollably, starting before birth.
Also found in: Dictionary, Thesaurus, Acronyms, Encyclopedia, Wikipedia.
Related to nevi: Melanocytic nevi, Dysplastic Nevi
?Note: This page may contain content that is offensive or inappropriate for some readers.
nevus
[
ne´vus] (pl.
ne´vi) (
L.)
a circumscribed stable malformation of the skin or sometimes the oral mucosa, which is not due to external causes; the excess (or deficiency) of tissue may involve epidermal, connective tissue, adnexal, nervous, or vascular elements. Most are either brown, black, or pink; they may appear on any part of the skin, vary in size and thickness, and occur either in groups or alone. See also mole.
A nevus is usually not troublesome unless it is unsightly or disfiguring or becomes inflamed. If it changes noticeably, malignancy may be suspected, especially if any of the following are present: a highly irregular border, an uneven (pebbly) surface, or a mixture of colors (especially black, gray, or blue). Any change in size, color, or texture, or any bleeding or excessive itching, should be reported to a health care provider. Nevi can be removed by surgery or by other methods such as the application of solid carbon dioxide, injections, or radiotherapy.
blue nevus a dark blue nodular lesion composed of closely grouped melanocytes and melanophages in the mid-dermis.
blue rubber bleb nevus a hereditary condition marked by multiple bluish cutaneous hemangiomas with soft raised centers, frequently associated with hemangiomas of the gastrointestinal tract.
nevus comedo´nicus a rare epidermal nevus marked by one or more patches 2 to 5 cm or more in diameter, in which there are collections of large comedones or comedolike lesions. This condition is occasionally associated with other lesions such as ichthyosis, vascular nevi, and cataracts.
compound nevus a nevocytic nevus composed of fully formed nests of nevus cells in the epidermis and newly forming ones in the dermis.
connective tissue nevus any nevus found in the dermal connective tissue with nodules, papules, plaques, or combinations of such lesions. Histologically, there is inconstant focal or diffuse thickening and abnormal staining of collagen.
epidermal nevus (epithelial nevus) a circumscribed congenital developmental anomaly resulting in faulty production of mature or nearly mature cutaneous structures; such nevi vary widely in appearance, size, and distribution and are commonly hyperkeratotic.
nevus flam´meus a congenital vascular malformation involving mature capillaries, present at birth. It consists of a reddish purple lesion that is flat or barely elevated and does not fade with age. It is a benign condition but may be associated with other syndromes such as sturge-weber syndrome. The dark variety is called a port-wine stain and a light variety is called a salmon patch. (See Atlas 1, Part E).
giant congenital pigmented nevus (giant hairy nevus) (giant pigmented nevus) any of a group of large, darkly pigmented hairy nevi, usually bilaterally symmetrical and present at birth; the most common locations are the chest, upper back, shoulders, arms, legs, and or hip and groin area. These nevi are associated with other cutaneous and subcutaneous lesions, as well as neurofibromatosis and other developmental anomalies, and they exhibit a predisposition to development of malignant melanoma.
halo nevus a pigmented nevus surrounded by a ring of depigmentation; called also leukoderma acquisitum centrifugum, Sutton's disease, and Sutton's nevus.
intradermal nevus a type of nevocytic nevus clinically indistinguishable from compound nevus, in which the nests of nevus cells lie exclusively within the dermis.
nevus of Ito a mongolian spot–like lesion having the same features as nevus of Ota except for localization to the areas of distribution of the posterior supraclavicular and lateral cutaneous brachial nerves, involving the shoulder, side of the neck, supraclavicular areas, and upper arm.
junction nevus (junctional nevus) a brownish, smooth, flat or slightly raised nevocytic nevus; histologically, there are nests of melanin-containing nevus cells at the dermoepidermal junction. (See Atlas 2, Part N.)
nevus lipomato´sus one that contains much fibrofatty tissue.
melanocytic nevus any nevus, usually pigmented, composed of melanocytes.
nevocytic nevus (nevus cell nevus) the most common type of nevus, usually more or less hyperpigmented, initially flat but soon becoming elevated, composed of nests of nevus cells. These nevi are classified as compound, intradermal, or junction according to the histologic pattern and location of nevus cells. Called also mole.
nevus of Ota (Ota's nevus) a persistent mongolian spot–like lesion, usually present at birth and unilateral, involving the conjunctiva and skin about the eye, as well as the sclera, ocular muscles, retrobulbar fat, periosteum, and buccal mucosa. It is a blue or gray-brown patchy area of pigmentation that grows slowly and becomes deeper in color. Although the lesion is benign, malignant melanoma occasionally develops, usually in the iris.
pigmented nevus (nevus pigmento´sus) one containing melanin; the term is usually restricted to nevocytic nevi (moles), but may be applied to other nevi that have pigmentation.
sebaceous nevus (nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn) an epidermal nevus of the scalp or less often the face, frequently growing larger during puberty or early adult life. In later life, some lesions may give rise to a variety of new growths, including basal cell carcinoma.
spider nevusvascular spider.
nevus spi´lus a smooth, tan to brown, macular nevus composed of melanocytes and speckled with smaller, darker macules.
spindle and epithelioid cell nevus a benign compound nevus occurring most often in children before puberty, composed of spindle and epithelioid cells located mainly in the dermis, sometimes in association with large atypical cells and multinucleate cells, and having a close histopathological resemblance to malignant melanoma.
nevus spongio´sus al´bus muco´saewhite sponge nevus.
nevus uni´us la´teris a wartlike epidermal nevus, ranging from flesh colored to brown, found in a linear, unilaterally distributed pattern; on the extremities, the lesions usually follow the long axis, and on the trunk, they usually have a transverse orientation.
vascular nevus (nevus vascula´ris) (nevus vasculo´-sus) any of various reddish swellings or patches on the skin due to hypertrophy of capillaries; the term includes nevus flammeus, strawberry hemangioma, blue rubber bleb nevus, vascular spider, and cavernous hemangioma.
white sponge nevus a spongy white nevus of a mucous membrane, occurring as a hereditary condition.
ne·vi
(
nē'vī),
[L.]
nevi
Plural of nevus, see there.
ne·vi
(
nē'vī)
[L.]
nevus
(ne'vus) (ne'vi?)
plural.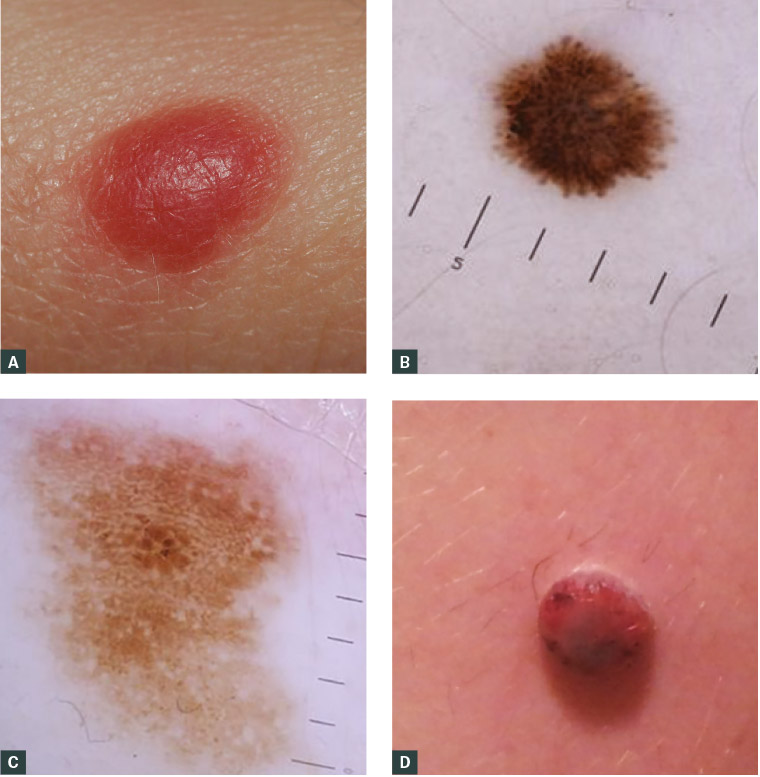 nevi
nevi [L.
naevus, birthmark]
1. A congenital discoloration of a circumscribed area of the skin due to pigmentation. Synonym: birthmark; mole
2. A circumscribed vascular tumor of the skin, usually congenital, due to hyperplasia of the blood vessels. See: angioma
nevus anemicus
A patch of pale skin in which blood vessels are narrowed or contracted and blood flow is locally limited.
nevus araneus
Spider angioma.
blue nevus
A dark blue nevus covered by smooth skin. It is composed of melanin-pigmented spindle cells in the mid-dermis.
blue rubber bleb nevus
An erectile, easily compressible, bluish, cavernous hemangioma present in the skin and gastrointestinal tract.
capillary nevus
A nevus of dilated capillary vessels elevated above the skin. It is usually treated by ligature and excision.
nevus comedonicus
A horny nevus that contains a hard plug of keratin. It is caused by failure of the pilosebaceous follicles to develop normally.
compound nevus
A cluster of melanocytes found in both the epidermis and the dermis.
connective tissue nevus
cutaneous nevus
A nevus formation on the skin.
dysplastic nevus
A nevus composed of cells having some malignant characteristics.
eclipse nevus
A benign nevus often found on the scalp, having a pale or tan center enclosed within a darker encircling rim.
epidermal nevus
Raised nevi present at birth. They may be hyperkeratotic and widely distributed.
faun tail nevus
In newborns, a tuft of hair over the lower spinal column. It may be associated with spina bifida occulta.
nevus flammeus
A large reddish-purple nevus of the face or neck, usually not elevated above the skin. It is considered a serious deformity due to its large size and color. In children, these have been treated with the flashlamp-pulsed tunable dye laser.
Synonym: port-wine mark; port-wine stain See:
illustrationhairy nevus
A nevus covered by a heavy growth of hair. It is usually darkly pigmented.
halo nevus
A papular brown nevus with an oval halo occurring in the first three decades of life. This type of nevus is usually benign but should be evaluated for malignancy.
intradermal nevus
A nevus in which the melanocytes are found in nests in the dermis and have no connection with the deeper layers from which they were formed.
Ito nevus
See: Ito nevus
junctional nevus
A nevus in the basal cell zone at the junction of the epidermis and dermis. It is slightly raised, pigmented, and does not contain hair. This type of nevus may become malignant. See: illustration
nevus lipomatous
A tumor composed of fatty connective tissue. It is probably a degenerated nevus containing numerous blood vessels.
Synonym: nevolipoma
melanocytic nevus
nevocytic nevus
A common mole. Moles may appear at any age. They are classified according to their stage of growth and whether or not they are still growing.
Ota nevus
See: Ota nevus
pigmented nevus
A congenital nevus varying in color from light yellow to black. Intradermal or nevocytic nevi are benign. Other types of nevi may become malignant. Synonym: nevus pigmentosus
Treatment
Malignant or suspicious lesions should be treated by wide surgical excision. Benign lesions do not require treatment except when located at sites of friction causing bleeding or ulceration. Some nevi are removed for cosmetic reasons. Arc rise fantasia on steam video.
nevus pigmentosus
pigmented nevus.
sebaceous nevus
nevus sebaceus.
nevus sebaceus
An epidermal nevus containing sebaceous gland tissue.
Synonym:
sebaceous nevusspider nevus
Spider angioma.
illustrationnevus spilus
A pigmented nevus with a smooth, unraised surface.
nevus spongiosus albus mucosae
White sponge nevus.
strawberry nevus
2. Infantile hemangioma.
telangiectatic nevus
nevus unius lateris
A congenital nevus that occurs in streaks or linear bands on one side of the body. It usually occurs between the neurotomes of the lumbar or sacral area.
vascular nevus
A nevus in which superficial blood vessels are enlarged. Nevi of this type are usually congenital. They are of variable size and shape, slightly elevated, and red or purple in color. They generally appear on the face, head, neck, and arms, though no region is exempt. The nevi usually disappear spontaneously, but wrinkling, pigmentation, and scarring are sometimes seen.
Synonym: strawberry nevus (1);
nevus vascularisnevus vascularis
Vascular nevus.
nevus venosus
Venous nevus.
venous nevus
Synonym:
nevus venosusverrucous nevus
A nevus with a raised, wartlike surface.
Synonym:
nevus verrucosusnevus verrucosus
Verrucous nevus.
white sponge nevus
A white, spongy nevus that may occur in the mouth, labia, vagina, or rectum. Synonym: nevus spongiosus albus mucosae
Nevus (plural, nevi)
The medical term for any anomaly of the skin that is present at birth, including moles and birthmarks.
Want to thank TFD for its existence? Tell a friend about us, add a link to this page, or visit the webmaster's page for free fun content.
Link to this page:
 nevi [L. naevus, birthmark]
nevi [L. naevus, birthmark] 